PHOBIA : TOMOPHOBIA
TOMOPHOBIA
- what is phobia?
A phobia is a type of anxiety disorder defined by a persistent and excessive fear of an object or situation. Phobias typically, result in a rapid onset of fear and are present for more than six months. Those affected will go to great lengths to avoid the situation or object, to a degree greater than the actual danger posed. If the object or situation cannot be avoided, they experience significant distress. Other symptoms can include fainting, which may occur in blood or injury phobia and panic attack, which are often found in agoraphobia. Around 75% of those with phobias have multiple phobias.
Phobias can be divided into specific phobia, social phobia and agoraphobia. Specific phobias include those to certain animals, natural environment situations, blood or injury, and specific situations. The most common are fear of spider, fear of snakes, and fear of heights. Specific phobias may be caused by a negative experience with the object or situation in early childhood. Social phobia is when a person fears a situation due to worries about others judging them. Agoraphobia is a fear of a situation due to a difficulty or inability to escape.
It is recommended that specific phobias be treated with exposure therapy in which the person is introduced to the situation or object in question until the fear resolves. Medications are not useful for specific phobias. Social phobia and agoraphobia are often treated with some combination of counselling and medication. Medications used include antidepressants, benzodiazepines, or beta-blockers.
Specific phobias affect about 6–8% of people in the western world and 2–4% of people in Asia, Africa, and Latin America in a given year. Social phobia affects about 7% of people in the United States and 0.5–2.5% of people in the rest of the world. Agoraphobia affects about 1.7% of people. Women are affected by phobias about twice as often as men. Typically, the onset of a phobia is around the ages of 10–17, and rates are lower with increasing age. Those with phobias are at a higher risk of suicide.
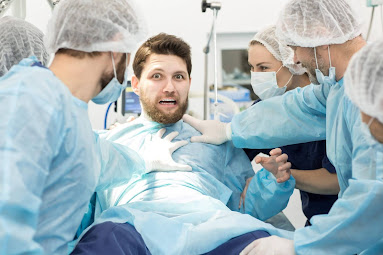
- many phobias in peoples like that there is tomophobia.
Most of us have some fear of medical procedures. Whether it’s worrying about the outcome of a test or thinking about seeing blood during a blood draw, being concerned about the state of your health is normal.
But for some people, that fear can become excessive and lead to avoidance of certain medical procedures, such as surgery. When this happens, their doctor may suggest being evaluated for a phobia called tomophobia.
- Tomophobia is the fear of surgical procedures or medical intervention.
While it’s natural to feel fear when you need to undergo a surgical procedure, therapist samantha chaikin, MA, says tomophobia involves more than the “typical” amount of anxiety expected. The avoidance of a medically necessary procedure is what makes this phobia very dangerous.
Tomophobia is considered a specific phobia, which is a unique phobia related to a specific situation or thing. In this case, a medical procedure.
While tomophobia isn’t common, specific phobias in general are quite common. In fact, the National Institute of Mental Health reports that an estimate above 12-15 percent of all nationas will experience a specific phobia in their lifetime.
Phobias affect personal relationships, work, and school, and prevent you from enjoying life. In the case of tomophobia, it means those affected avoid necessary medical procedures.
What makes phobias debilitating is that the fear is out of proportion or more severe than what would be reasonably expected given the situation. To avoid anxiety and distress, an individual will avoid the triggering activity, person, or object at all costs.
Phobias, regardless of the type, can disrupt daily routines, strain relationships, limit the ability to work, and reduce self-esteem.
Like other phobias, tomophobia will produce general symptoms, but they’ll be more specific to medical procedures. With that in mind, here are some general symptoms of a phobia:
- strong urge to escape or avoid the triggering event
- fear that is irrational or excessive given the level of threat
- shortness of breath
- chest tightness
- rapid heartbeat
- trembling
- sweating or feeling hot
For someone with tomophobia, it’s also common to:
- have situation-induced panic attacks when medical procedures need to be performed
- avoid the doctor or potentially lifesaving procedure due to fear
- in children, scream or run out of the room
The main cause of tomophobia is a traumatic experience with surgeries. For example, having undergone an operation where complications have occurred, suffering from the after-effects of an operation, medical malpractice, difficulty waking up, a lot of pain, etc.
Tomophobia can also be acquired by vicarious conditioning, if you see someone suffering a lot for an operation. Finally, the stories we hear about medical malpractice, operations that did not go well, etc., can also have a lot to do with the origin of tomophobia.
On the other hand, other phobias related to medical situations can also affect the onset of tomophobia (or coexist with it), such as: blood phobia (hemophobia or hematophobia), phobia during injections (trypanophobia), phobia in hospital, phobia among doctors, etc.
Tomophobia is diagnosed by a mental health professional, such as a psychologist.
Since tomophobia isn’t included in the most recent edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), an expert will likely look at specific phobias, which are a subtype of anxiety disorders.
specific phobia are broken down into five types:
- animal type
- natural environment type
- blood-injection-injury type
- situational type
- other types
The treatment of tomophobia, like that of any phobia, mainly focuses on two types of therapy: exposure therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy. Here, however, we will also look at a third: psychoeducational techniques.
1. EXPOSURE THERAPY (AND VIRTUAL REALITY)
In the case of exposure therapy applied to tomophobia, it’s a bit complex, like how to simulate a medical operation to expose the patient? It’s difficult; this is why, in this particular case, we can go to virtual reality (VR) exposure therapy.
This type of therapy, more and more widespread, simulates fictitious situations using technology. The patient can feel the sensations associated with the phobic stimulus quite realistically, and has the positive side that he is never in danger and can always “escape” the situation.
This type of therapy is used more and more, which is ideal for certain phobias where the phobic object is difficult to simulate, to represent or to use, as it would be the case with tomophobia.
2. COGNITIVE-BEHAVIORAL THERAPY
In contrast, cognitive behavioral therapy used for cases of tomophobia, would focus on eliminate or modify negative and irrational thoughts that the patient has in relation to the surgical operations, In addition to adopting habits of stress management and prevention.
In other words, it would be that he could rationalize his fears and replace the catastrophic thoughts with more realistic ones. Examples of thoughts associated with tomophobia, which should be examined by the patient, are: “if I go for surgery I will die”, “if I go for surgery I will not wake up”, “I will get worse. entering “,” my body will not take it “, etc.
3. PSYCHOEDUCATION AND OTHER TECHNIQUES
Using (and teaching) specific strategies for dealing with anxiety will also be important, By being for example: relaxation techniques, breathing, meditation, pleasant images …
In the case of children with tomophobia, one can opt for symbolic modeling techniques (through videos, stories … where fictitious characters undergo successful surgeries).
It will also be practical to conduct psychoeducation sessions, so that the patient understands the operation to be performed (if this is the case). In addition, in the latter case, it will be important to remove any doubt about the operation to which it must be subjected, so that multidisciplinary.






Nice
ReplyDeleteNice article bhai
ReplyDeleteGreat broo
ReplyDeleteBhout accha h bhaii
ReplyDelete